Hyperbaric Oxygenation Effects on Blood Flow
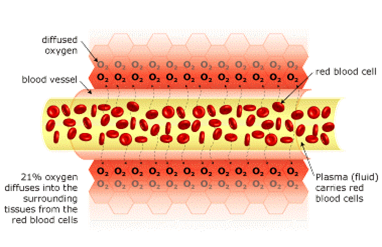
Normal Blood Flow
There is 21% oxygen in the air that we breathe. Our lungs transfer this oxygen to our red blood cells (via hemoglobin). These oxygen-filled red blood cells are carried around the body by the plasma (fluid), which travels through the blood vessels. The oxygen diffuses into the surrounding tissue ensuring that it is delivered to where it is needed most.
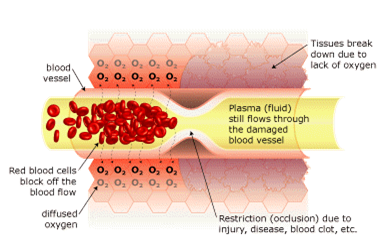
Restricted Blood Flow (Ischemia) Causes Hypoxia
When there is a restriction (occlusion) in blood flow due to surgery, illness, or injury, the red blood cells block the blood vessel and are unable to transfer oxygen to the cells on the other side of the occlusion. This causes swelling and starves the area of oxygen, causing hypoxia (a lack of oxygen); when this occurs, the tissue begins to break down. Hypoxia triggers ‘apoptosis’ (programmed cellular degeneration – clumping and clustering of damaged nerve cells surrounded by healthy neuronal tracts).
Image of apoptosis retrieved from https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/health-sciences-and-technology/hst-176-cellular-and-molecular-immunology-fall-2005/
Apoptosis reduces the ability of the body to repair itself. Apoptotic bodies and altered DNA fragmentations are observed in the ischemic region with increased inhibitory proteins released into the damaged areas, causing further deterioration. Apoptosis has been identified in all degenerative disorders including brain and spinal cord injury. Apoptosis fosters the cycle of continued dysfunction, degeneration, and ultimate celll death.
Apoptosis reduces the ability of the body to repair itself. Apoptotic bodies and altered DNA fragmentations are observed in the ischemic region with increased inhibitory proteins released into the damaged areas, causing further deterioration. Apoptosis has been identified in all degenerative disorders including brain and spinal cord injury. Apoptosis fosters the cycle of continued dysfunction, degeneration, and ultimate celll death.

Image of apoptosis retrieved from https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/health-sciences-and-technology/hst-176-cellular-and-molecular-immunology-fall-2005/

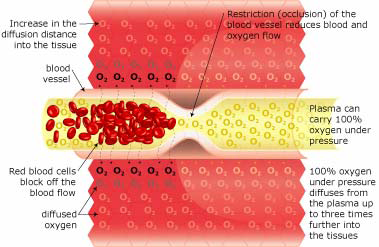
Hyperbaric Oxygenation
Breathing 100% oxygen under pressure causes the oxygen to diffuse into the blood plasma. This oxygen-rich plasma is then able to travel past the restriction, diffusing up to 3 times further into the tissue. The pressurized environment helps to reduce swelling and discomfort, while providing the body with at least 10-15 times its normal supply of oxygen. This helps repair tissue damaged by the original occlusion or subsequent hypoxic condition.
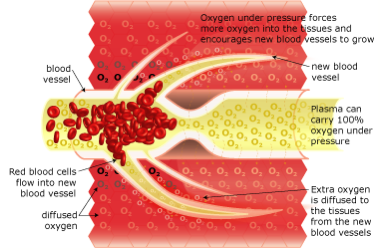
Neurovascular Regeneration
HBOT directly and dramatically increases tissue oxygenation, slowing and reversing hypoxic induced apoptosis. HBOT also restores blood supply to the compromised region by the generation of new capillary networks (neovascularization), enabling the body to alter the course and impact of the disease and injury process.
HBOT mobilizes the body’s circulating stem cells. American Journal Physiology – Heart and Circulatory Physiology (Nov 05)] reports a single 2-hour exposure to HBOT at 2 ATA doubles the amount of circulating CD34+ progenitor stem cells (primordial cells targeted to salvage and restore damaged structures); and at approximately 40-hours of HBOT; circulating CD34+ cells increase eight-fold (800%).
Advanced Healing One Breath at a Time
Begin your healing today.